In today’s fast-paced world, knowing how much sleep your body needs is crucial to maintaining optimal health and function.
Understanding your sleep requirements can help you avoid chronic fatigue, improve your mood, and boost your overall well-being.
So, are you getting enough sleep?
Let’s explore the recommended hours of sleep for different age groups and discover the key factors that may affect your personal sleep needs.
Review contents
Importance of Sleep
Getting enough quality sleep is crucial for maintaining good health and overall well-being. Sleep is vital in various aspects of our lives, including physical, mental, and emotional health.
When you consistently get the recommended amount of sleep, you can experience numerous benefits that positively impact your daily life.
On the other hand, depriving yourself of sleep can seriously affect your overall health and functionality.
Benefits of getting adequate sleep
When you prioritize and consistently obtain adequate sleep, you allow your body and mind to rejuvenate and repair themselves.
Here are some key benefits of getting enough sleep:
- Improved physical health: Sleep is essential for your body’s recovery and rejuvenation, helping to reduce the risk of various health conditions, including heart disease, obesity, and diabetes. It strengthens your immune system, allowing it to fight off infections and illnesses effectively.
- Enhanced cognitive function: A good night’s sleep promotes better concentration, attention, and memory. It allows your brain to process and consolidate information, improving learning abilities and problem-solving skills.
- Emotional well-being: Sufficient sleep helps regulate your mood and emotions. It increases your resilience to stress and promotes better emotional stability, reducing the risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
- Increased productivity and creativity: When well-rested, you experience improved productivity, efficiency, and creativity. Your ability to focus and make effective decisions is heightened, leading to better performance in work and daily activities.
- Weight management: Sleep plays a role in regulating appetite hormones. Sufficient sleep can help prevent overeating and weight gain, as it promotes a healthy balance of these hormones.
Consequences of sleep deprivation
Conversely, neglecting your sleep needs can seriously affect your overall health and functionality.
Here are some of the adverse effects of sleep deprivation:
- Impaired cognitive function: Lack of sleep negatively affects your ability to concentrate, problem-solve, and make decisions. It impairs your memory and reduces your reaction time, increasing the risk of accidents and mistakes.
- Mood disturbances: Sleep deprivation often leads to irritability, mood swings, and increased susceptibility to stress. It can contribute to developing or worsening mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
- Weakened immune system: Inadequate sleep weakens your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections, viruses, and chronic illnesses. It can also prolong the duration of illnesses when you do get sick.
- Increased risk of chronic conditions: Sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of developing chronic health conditions, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer.
- Impaired physical performance: Lack of sleep affects your coordination, motor skills, and physical performance. It decreases your strength and endurance, making it more challenging to engage in physical activities.
Factors Influencing Sleep Needs
The amount of sleep each person needs can vary based on various factors. +
Understanding these factors can help you determine your sleep needs and develop healthy sleep habits. Here are some key factors that influence sleep needs:
Age
Age is one of the most significant factors that influence sleep needs. As we go through different stages of life, our sleep requirements change. Infants and young children need more sleep, while teenagers and adults need slightly less. Older adults may find their sleep patterns changing due to age-related factors.
Overall health
Your overall health plays a role in determining your sleep needs. Chronic illnesses, pain, and certain medical conditions can disrupt your sleep, requiring you to get more rest to support your body’s healing and recovery processes.
Lifestyle and daily activities
Your lifestyle and daily activities also impact your sleep needs. Those who engage in physically demanding work or exercise may require more sleep to allow their bodies to recover.
Similarly, individuals with mentally demanding jobs or engaging in intense mental activities may need additional sleep to support cognitive function.
Genetics and individual differences
Genetics and individual differences contribute to variations in sleep needs. Some people may naturally require more sleep, while others function well with less sleep.
It’s essential to listen to your body’s signals and determine what works best for you.
Recommended Sleep Duration
While the exact sleep duration needed can vary from person to person, several organizations provide general guidelines to help individuals determine their optimal sleep duration.
One such organization is the National Sleep Foundation (NSF). They offer age-specific recommendations as a starting point for understanding the amount of sleep needed.
National Sleep Foundation’s guidelines
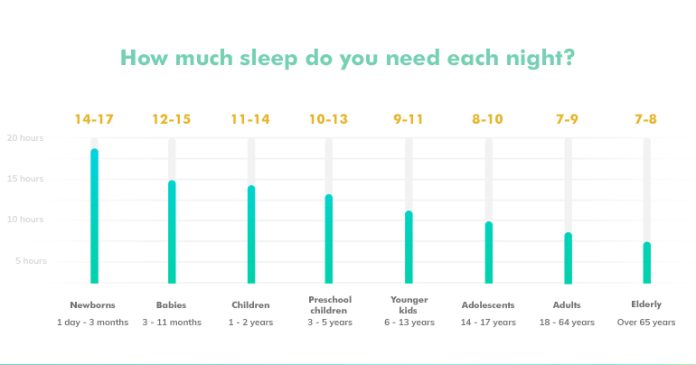
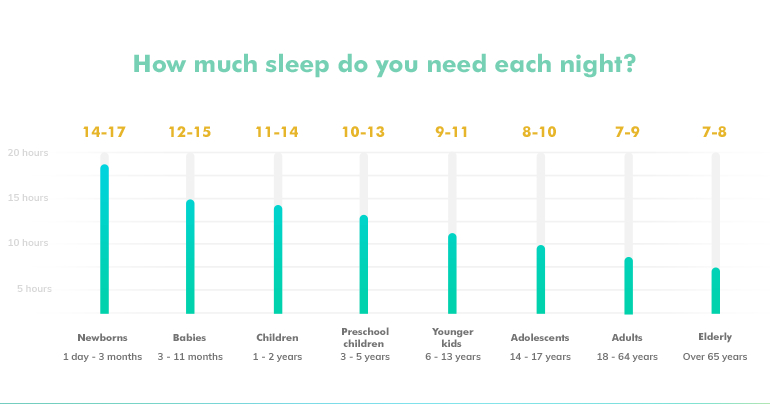
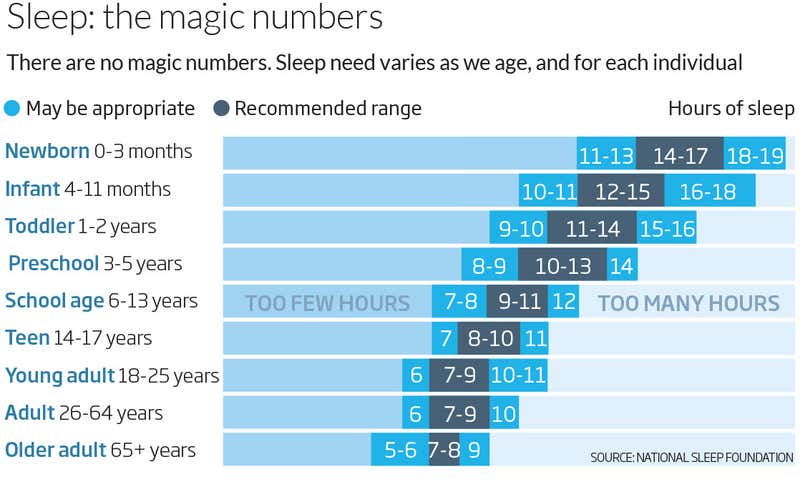
The National Sleep Foundation recommends the following sleep durations for different age groups:
- Newborns (0-3 months): 14-17 hours
- Infants (4-11 months): 12-15 hours
- Toddlers (1-2 years): 11-14 hours
- Preschoolers (3-5 years): 10-13 hours
- School-age children (6-13 years): 9-11 hours
- Teenagers (14-17 years): 8-10 hours
- Young adults (18-25 years): 7-9 hours
- Adults (26-64 years): 7-9 hours
- Older adults (65+ years): 7-8 hours
These recommendations serve as general guidelines and may not apply to everyone. It’s essential to consider individual differences and listen to your body’s signals about the amount of sleep you need.
Age-specific recommendations
As seen in the NSF’s guidelines, sleep needs evolve as we age. Infants and young children require more sleep for growth and development, while older adults require slightly less sleep. Understanding age-specific recommendations can help you prioritize sleep accordingly.
Critical considerations for determining optimal sleep duration
While age-specific recommendations provide a helpful starting point, it’s essential to consider individual factors when determining optimal sleep duration.
Factors such as overall health, lifestyle, and daily activities play a role in influencing your sleep needs. Listening to your body and adjusting your sleep duration can help ensure you get the restorative sleep you need.
Sleep Needs by Age Group
Sleep requirements vary across different age groups due to the ongoing physical, mental, and emotional changes. Here’s a breakdown of sleep needs by age group:
Infants (0-3 months)
During their first few months, infants require the highest amount of sleep. Newborns typically sleep about 14 to 17 hours a day, although their sleep is fragmented into shorter periods. They have irregular sleep-wake cycles and wake frequently for feeding and diaper changes.
Babies (4-12 months)
As babies grow, their total sleep duration decreases slightly. Babies aged 4 to 11 months need about 12 to 15 hours of sleep daily. They may have a more structured sleep schedule and more extended periods of nighttime sleep. However, they still require several naps throughout the day.
Toddlers (1-2 years)
Toddlers typically require around 11 to 14 hours of sleep per day. This includes nighttime sleep and one or two daytime naps. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and schedule is essential at this age to promote healthy sleep habits.
Preschoolers (3-5 years)
Preschoolers generally need about 10 to 13 hours of sleep each night. They may start to outgrow daytime naps, but some may still benefit from a short nap. Consistency in bedtime routines and sleep schedules supports healthy development and learning.
School-age children (6-13 years)
As children enter school age, their sleep needs decrease to approximately 9 to 11 hours per night. Establishing a regular sleep schedule and limiting evening screen time is essential to ensure they get sufficient rest for optimal academic performance and overall well-being.
Teenagers (14-17 years)
Teenagers require about 8 to 10 hours of sleep per night during adolescence. However, due to hormonal changes and a shift in their internal body clock, many teenagers may experience difficulty falling asleep early in the evening. Creating a sleep-friendly environment and practicing good sleep hygiene can help improve sleep quality.
Young adults (18-25 years)
Young adults typically need approximately 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night. However, this age group often faces challenges in prioritizing sleep due to busy schedules and lifestyle factors. Young adults need to recognize the importance of sleep and establish healthy sleep habits for overall well-being.
Adults (26-64 years)
The recommended sleep duration for adults is about 7 to 9 hours per night. However, individual variations can exist, and some adults may function well on slightly less sleep. Prioritizing sleep becomes increasingly important during this stage of life to support overall health and energy levels.
Older adults (65 years and older)
As individuals age, their sleep patterns may change, including a shift towards lighter and more fragmented sleep. Older adults typically require about 7 to 8 hours of sleep per night. Older adults must establish good sleep habits and seek treatment for any sleep disorders or conditions affecting their sleep quality.
Impact of Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders can significantly disrupt sleep patterns and negatively impact overall health and well-being. Here are some common sleep disorders and their impact:
Insomnia
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non-refreshing sleep. It can lead to daytime fatigue, irritability, and decreased cognitive function.
Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is when breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. It can disrupt a person’s sleep, leading to daytime sleepiness, reduced alertness, and an increased risk of cardiovascular problems.
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. It can cause excessive daytime sleepiness and uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep.
Restless legs syndrome
Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. RLS can disrupt sleep and lead to daytime fatigue and discomfort.
Other common sleep disorders
Other common sleep disorders include sleepwalking, night terrors, REM sleep behavior, and circadian rhythm disorders. These disorders can result in impairments in sleep quality and daytime functioning.
Sleep Debt and Catching Up
Understanding the concept of sleep debt and catching up can help individuals prioritize their sleep needs. Here’s what you need to know:
Understanding sleep debt
Sleep debt is the accumulated amount of sleep owed to your body when you consistently get less than your optimal sleep duration. For example, if you require 8 hours of sleep per night but only get 6 hours for several nights, you accumulate a sleep debt of 4 hours.
The concept of sleep debt recovery
While it’s impossible to ultimately “pay off” sleep debt by sleeping longer on weekends or rest days, you can partially compensate for it.
Catching up on sleep by getting additional rest during non-work or non-busy periods can help reduce the impacts of sleep debt on your overall well-being.
Strategies for catching up on sleep
To catch up on sleep and reduce sleep debt, prioritize longer sleep duration during days off or weekends.
Aim to gradually increase your total sleep time until you feel adequately rested. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can help prevent further accumulation of sleep debt.
Effects of Poor Sleep Quality
Poor sleep quality can significantly affect our daily functioning even when we achieve the recommended sleep duration. Here are some common effects of poor sleep quality:
Daytime drowsiness and fatigue
When sleep quality is compromised, you may experience increased daytime drowsiness, fatigue, and a lack of energy. This can impact your ability to focus, concentrate, and perform effectively throughout the day.
Cognitive impairment and memory problems
Poor sleep quality can impair cognitive function, including memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities.
It can make retaining and processing information challenging, impacting learning and academic or professional performance.
Emotional disturbances
Sleep disturbances can contribute to emotional instability, irritability, mood swings, and an increased risk of developing or exacerbating mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety.
Compromised immune function
Inadequate sleep quality weakens the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections, viruses, and illnesses. It can prolong the duration of illnesses and hinder your body’s recovery.
Increased risk of chronic conditions
Research suggests poor sleep quality is associated with an increased risk of developing chronic health conditions such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer. Addressing sleep quality is essential in maintaining overall health.
Individual Variations in Sleep Needs
While there are general sleep recommendations, it’s essential to recognize that individual variations in sleep needs exist. Here are a few factors that contribute to these variations:
Short sleepers vs. long sleepers
Some individuals naturally require less sleep and function well on a shorter sleep duration. These individuals are often referred to as “short sleepers.”
On the other hand, some individuals may naturally need more sleep to feel rested and function optimally. They are known as “long sleepers.” Understanding which category you fall into can help you establish optimal sleep duration.
Effect of environmental factors on sleep requirements
Environmental factors, such as temperature, noise levels, and light exposure, can significantly affect sleep quality and needs. Some people are more sensitive to these factors and may require specific adjustments to their sleep environment to optimize their rest.
The importance of listening to your body
Listening to your body’s signals and cues is crucial in determining your sleep needs. Pay attention to how you feel after different sleep durations and adjust accordingly. If you consistently feel tired or dizzy, it may indicate that you need more sleep.
Determining Your Optimal Sleep Duration
Finding your optimal sleep duration involves self-assessment and experimentation. Here are some strategies to determine your sleep needs:
Keeping a sleep diary
Maintaining a sleep diary can help you track your sleep patterns, including bedtime, wake-up time, and sleep quality. Note how you feel upon waking and throughout the day to identify patterns and determine the optimal sleep duration that leaves you feeling well-rested.
Experimentation and self-assessment
Experiment with different sleep durations and observe how you feel and function with each duration.
Gradually increase or decrease your sleep duration and assess any changes in alertness, mood, energy levels, and overall well-being. Use this information to determine your optimal sleep duration.
Consulting with healthcare professionals
If you’re struggling to determine your optimal sleep duration or are experiencing persistent sleep issues, consider consulting with healthcare professionals, such as sleep specialists or primary care physicians.
They can provide guidance, conduct evaluations, and recommend necessary interventions.
Creating Healthy Sleep Habits
Establishing healthy sleep habits, also known as sleep hygiene, can help optimize the quality and duration of your sleep. Here are some essential practices to promote healthy sleep:
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule
Consistency is vital when it comes to sleep. Try to go to bed and wake up simultaneously each day, even on weekends or days off. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep quality.
Creating a relaxing sleep environment
Design your bedroom to be a sleep-friendly space. Make sure the room is calm, dark, and quiet. Use comfortable bedding, invest in a supportive mattress and pillow, and remove distractions like electronics emitting blue light.
Limiting stimulants and electronic device usage
Avoid consuming stimulants such as caffeine or nicotine close to bedtime, as they can interfere with falling asleep.
Additionally, limit your use of electronic devices in the evening, such as smartphones and tablets, as they emit blue light that can suppress the sleep-inducing hormone melatonin.
Engaging in regular exercise
Regular physical activity can promote better sleep quality. Aim to moderate-intensity exercise for at least 30 minutes most days of the week. However, avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as it can make it challenging to fall asleep due to increased alertness.
Practicing relaxation techniques
Incorporate relaxation techniques into your nighttime routine to prepare your mind and body for sleep.
This can include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, or reading a relaxing book. Find what works best for you and make it a consistent bedtime routine.
By implementing these healthy sleep habits, you can create an optimal sleep environment and support the quality and duration of your sleep, improving overall well-being and functionality in your daily life. Remember, prioritizing sleep is essential for leading a healthier and more fulfilled life.